A cryptocurrency is a type of currency that uses digital files as currency based on an open, distributed ledger that records transactions in codes called blockchain technology. Usually, in cryptocurrency, the files are created using the same methods as cryptography (the science of hiding information). Cryptocurrency uses “decentralized control”, which means that it is not controlled by a single person or government. This new currency technology is not bound by geography because it is internet-based, some of the most renowned currencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, XRP, Cardano, EOS, Monero, etc… but Bitcoin leads the pack in Africa and worldwide.
Current situation of Cryptocurrency in Africa
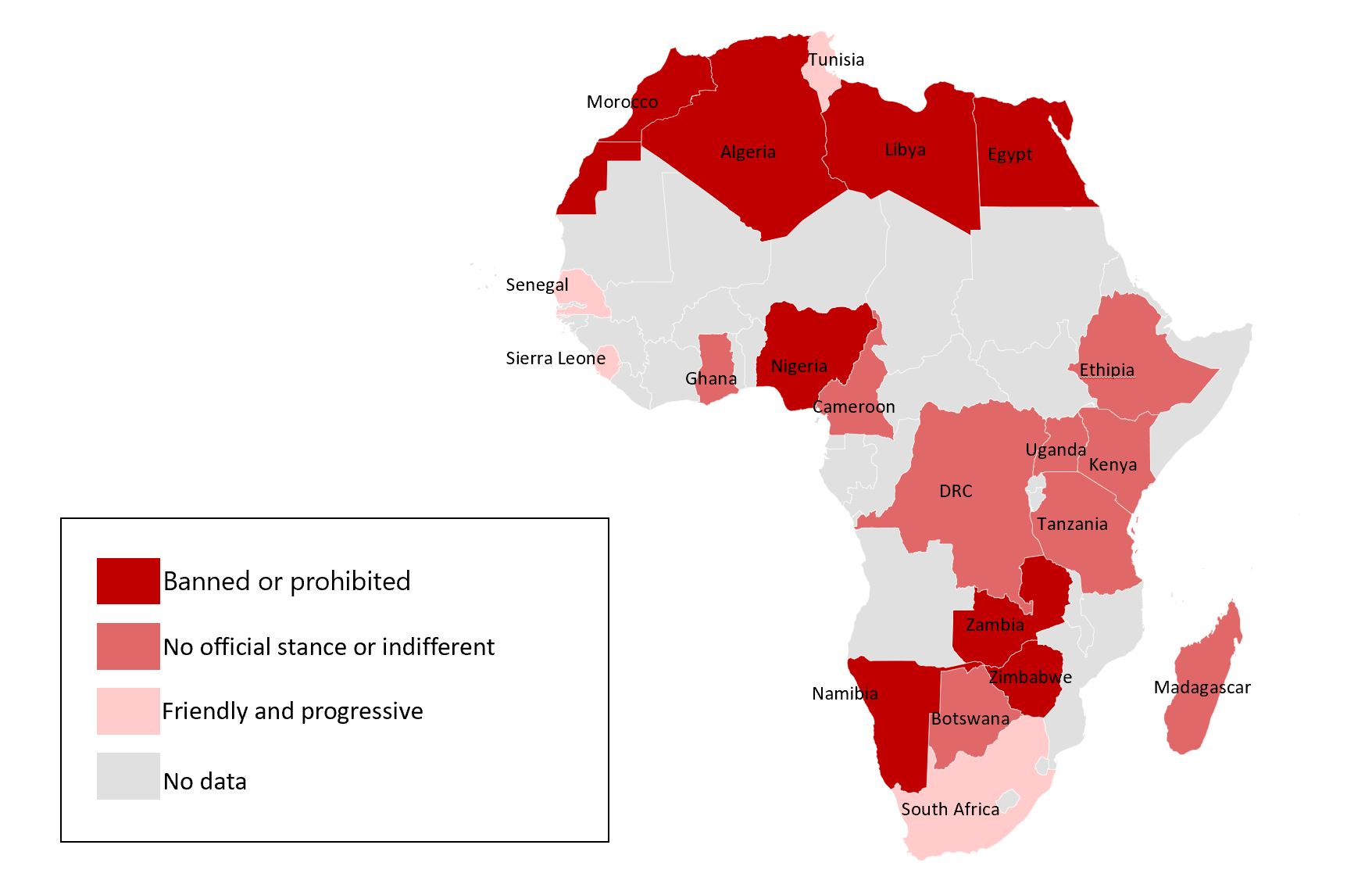
Africa does not have a very big market for Cryptocurrency but it is growing despite the concerns people have and tough regulations in different countries. According to BitcoinAfrica.io, the top 5 African countries whose communities are adopting Bitcoin are South Africa, Nigeria, Zimbabwe, Kenya, and Ghana. They have the most demand for digital currency as well as the most active local cryptocurrency communities. In addition, according to bitcoin.com South Africa, Nigeria and Kenya appear in the top 10 countries by Cryptocurrency Adoption worldwide. Does that reflect how African governments are adopting this new technology? Nigeria has one of the most dynamic peer-to-peer Bitcoin trading markets in the world, but so far the country has banned Cryptocurrency and warned its citizens that Bitcoin investments had no legal cover. On January 12, 2017, the CBN (Central Bank of Nigeria) warned all the Banks and Financial institutions in Nigeria to never use, hold, trade, or transact any virtual currency. On the 5th of February 2021, the CBN has ordered banks across the country to close the accounts of anyone who deals in cryptocurrency. Not only Nigeria but also Morocco, Algeria, Libya, Egypt, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Namibia have banned the use of cryptocurrency. In Kenya, the government is neither receptive nor prohibiting cryptocurrency, however, they also warn their citizens that it is not legal tender, so they do not provide any protection for any failure that can appear in the cryptocurrency businesses. In South Africa, there are no specific laws or regulations that address the use of virtual currencies, however, they have made a Crypto Assets Regulatory Working Group that is reviewing the country’s position on crypto assets.
Why does cryptocurrency keep growing in Africa despite the challenges?
The economic instability in Africa is one of the reasons Africans are transitioning to cryptocurrency. Companies like Bitcoin do not have a single domain, the money traded by the company is not affected by inflation rates of a single country, which allows citizens of African countries to protect their earnings from a failing economy. Besides, cross-border payment is easier with Bitcoin. For example, Paypal was once banned in Nigeria as a result of fraudulent and money laundering activities, but Cryptocurrency companies use blockchain technology that stores public records in a decentralized system. This means that they cannot ban the transaction from a single country. In addition, cryptocurrency transactions are quick with lower transaction costs and there are no intermediaries as they are decentralized. Finally, they are cryptographically secure. Business owners in Africa often want to run their businesses on an international scale. Some of these businesses started to use blockchain and cryptocurrency in order to grab the international market’s attention and protect businesses against currency devaluation. So, the banning of cryptocurrency by the government can not stop the online transactions of virtual currency.
Some of the African businesses that have adopted the cryptocurrency technology in their transaction.
Akoin
Eager to improve financial stability in Africa while providing a secure monetary system and, in fine, boost economies, the worldwide Senegalese singer Akon has launched, in 2018, a new cryptocurrency branded Akoin. This currency aims to represent the economical basis of the Akoin Ecosystem, a future smart city project close to Dakar, extended on 2 000 ha, gathering digital projects. As part of the Akoin Ecosystem, consumers will be able to buy, save and spend their Akoin directly with their application to be available on each mobile phone by December. Surrounded by computer engineers, the worldwide singer ensures the cryptocurrency Akoin will be based on cryptography to secure and verify transactions and make it impossible to counterfeit. This initiative is the continuation of Akon’s actions in Africa, which provided solar energy solutions in 18 African countries already, through his Akon Lighting Africa foundation.
Bankymoon
Bankymoon is a software and consulting firm with expertise in Blockchain technologies from South Africa. They develop bespoke solutions for clients who require Bitcoin and other crypto-currency integrations. Bankymoon has launched prepaid blockchain smart meter technology as a solution to electrical utilities struggling to collect revenue and African consumers lacking formal banking facilities. They integrated Bitcoin payments into smart metering systems that allow users anywhere in the world to send electricity, water, and gas to any recipient to top up their utility meters.
BuyCoins
Created in 2017, BuyCoins is the only exchange platform in Nigeria that allows Nigerians to buy and sell cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and Bitcoin Cash) directly with their local bank account or debit card, instantly with no wait time. BuyCoins developed thanks to the Y Combinator Summer 2018 program.
After the CBN’s order on the 5th Feb 2021, prohibiting the Nigerian Deposit Money Banks (DMBs), Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NBFs), and Other Financial Institutions (OFIs) from working with cryptocurrency exchanges. Buycoins found a workaround to help their customers, they no longer directly accept deposits or process withdrawals in Nigeria but they introduced P2P (peer-to-peer) deposits & withdrawals by matching user deposits to user withdrawal requests. Here is how this alternative works according to medium.com:
- User A wants to deposit N5000.
- User B wants to withdraw N5000.
- BuyCoins matches these two requests.
- The depositor (User A) is directed to make a transfer to User B using a payment method of their choice.
- Upon confirmation of receipt of payment, BuyCoins debits the withdrawer’s (User B) BuyCoins NGNT balance and credits the depositor.
Sun Exchange
The Sun Exchange makes it possible for South African businesses and individuals to buy solar panels and to lease them to companies, farmers, or schools. This project allows the growth of innovative solar panel networks thanks to mobile payments, online payment, and the use of cryptocurrencies.
LEAF
LEAF is a Rwandan company that is developing a platform of mobile applications to facilitate the conversion of currency into virtual currency via blockchain technology, dedicated to the population that does not have access to banks in Africa.
Bitmama
Launched in 2018, Bitmama is a Nigerian fintech company that allows people to trade by converting their local currency to cryptocurrency. It provides a platform for traders to exchange their fiat currency directly with digital money like Bitcoin, Dash, and Ether. It allows its users to create their own wallets and start buying or selling digital currencies by connecting with their bank accounts, credit or debit cards, and mobile money accounts. It also offers institutions and professionals the ability to trade a variety of digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum.
“At Bitmama, we place customer satisfaction over everything we do. We have released several communications to our customers educating them about the ban and how it affects some services such as naira deposits and withdrawals while providing alternate solutions. Our customers have been assured that their money is safe and they can access it anytime.” Said the Bitmama CEO to nigeriatodaynews.com after the ban of the cryptocurrency in Nigeria
Centbee
Centbee is an innovative South African Bitcoin start-up with global ambitions. It is a payment company specializing in merchant payments, cross-border remittances, and other cryptocurrency-related products. Thanks to its mobile wallet, it allows users to make transactions with Bitcoin SV, making it easy to spend, receive, and store the Bitcoin SV.
Cajutel
Cajutel, a Swiss Internet access provider, aims at deploying its Internet broadband in Guinea-Bissau through virtual currency fundraising. This Internet broadband network is to be fueled by solar energy: which will not only reduce its dependency on electric energy which often harms the availability of the service, but also its costs by not using fuel when the electric network fails. The company intends to fund this large-scale project through a virtual currency fundraising: the “Ether” with 720 000 tokens and 60 000 added actions to check out allowances and advertising costs. A million tokens are to be retained by existing shareholders. In total, 1,78 million tokens will be circulating. In constructing a solar-fueled high-tech broadband Internet network, Cajutel aims at becoming a reference at providing access to high-quality Internet access at reasonable prices.
Cryptocurrency challenges in Africa
Resistance from regulators is one of the biggest challenges in Africa as stated in the paragraphs above but digital literacy in Africa is also a barrier. Read also Digital literacy in Africa. Since cryptocurrency currently uses the internet to be processed and the internet penetration in Africa is still low, African citizens will find it hard to exchange cryptocurrencies. However, according to bitcoin.com, there is also an increasing focus on the transmission of encrypted payments without Internet connectivity. To date, Blockstream has been the pioneer in this field, creating a satellite network with global coverage that broadcasts the Bitcoin network for free.
Cryptocurrency is not only a solution for the fate of the “unbanked”. On the contrary, it is a method to economically allow the population to control their own wealth. The intangible nature of digital currencies means that a government cannot physically remove the wealth of a citizen. Successful adoption of mobile money in Africa can either be a good starting point for a citizen to understand and adopt cryptocurrency or be a comfort zone for the citizen who wants to trade digitally and refuse to try the new technology. While mobile money services rely on a centralized business model to operate, extracting fees and revenues from customers, cryptocurrency is decentralized and has the potential to offer almost-free transactions.
Did you know?Research done by the energy tariff comparison service shows that the amount of energy expended mining Bitcoin globally has already exceeded the amount used on average by Ireland and most African nations and is more than the annual usage of almost 160 countries. Miners are resorting to more and more powerful computers to complete these tasks and earn Bitcoin and as a result, mining (and on the flip side, Bitcoin transactions) are using up greater and greater amounts of electricity. In fact, according to Dutch Bank ING, a single Bitcoin trade consumes as much electricity to power a house for a whole month. |

